Heat transfer printing is a widely used method for transferring designs onto various surfaces. Whether it’s on fabrics, ceramics, or even metals, this printing process offers versatility and durability. In this article, we will delve into the process of heat transfer printing, exploring its steps, applications, and advantages.
How does Heat Transfer Printing Work?
Heat transfer printing is a process of transferring a design from a special paper to a fabric or other surface using heat and pressure. The design is first printed onto the transfer paper using a heat transfer printer. The transfer paper is then placed on the fabric or other surface and a heat press is used to apply heat and pressure. The heat melts the waxy ink on the transfer paper, which then bonds to the fabric or other surfaces.
Materials Used in Heat Transfer Printing
A printer is used for the heat transfer printing process, but it requires special inks to work. A wax-based ink is required. The ink ribbon together, and an image is created from the printer. Heat transfer printing uses the process of heat to transfer by a heat press where the image created in wax and transferred to an object or garment.
Heat Transfer Printing Process Step by Step
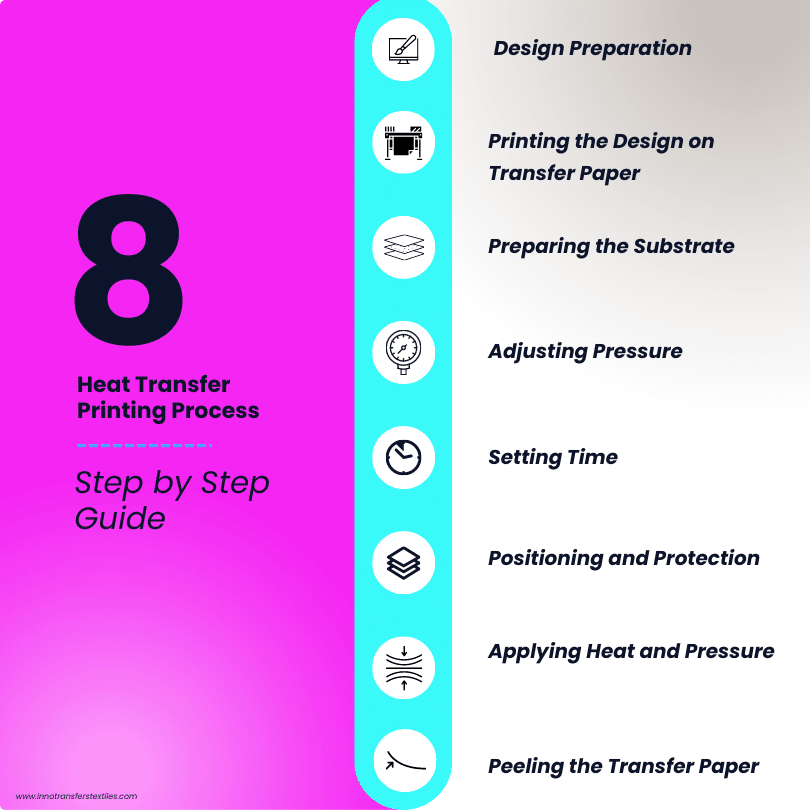
Design Preparation
The heat transfer printing process begins with designing or selecting the desired image or pattern. This design is then prepared using graphic design software. The most used graphic design software used for making designs is Adobe illustrator which is far more the best for making vector graphics. It’s essential to ensure that the design is in a suitable format and resolution for optimal printing results. Check out Inntransfers Artwork Guidelines for requirements of your design.
Printing the Design on Transfer Paper
Once the design is ready, it is printed onto transfer paper using a specialized printer and ink. If you do not have a heat transfer printer, you can purchase transfer paper from Innotransfers with your required designs.The printer applies the design in reverse, as it will be mirrored during the transfer process. High-quality transfer paper is crucial for achieving sharp and vibrant prints.
Preparing the Substrate
The substrate, or the material onto which the design will be transferred, needs to be prepared before applying heat and pressure. This typically involves pre-washing fabrics to remove any dirt, oils, or sizing agents that could hinder the transfer process. For other surfaces, such as ceramics or metals, cleaning and priming may be necessary.
Adjusting Pressure
The pressure of the press should be based on the thickness of the fabric you’re using. Thicker fabric requires less pressure, while thinner fabric may need a bit more. For most projects, set the pressure to medium or high.
Setting Time
Different types of heat transfer require specific timing. Use the following as a guide:
- Inkjet Transfer Paper: 14 – 18 seconds
- Dye Sublimation Transfer: 25 – 30 seconds
- Digital Appliqué Transfer: 20 – 30 seconds
- Vinyl Transfer: 45 – 60 seconds
Check out our Unit transfers, Compatible with any heat press in the market/printing in 4 only seconds with the Innoprinter..
Positioning and Protection
Place your product onto the heat press machine’s plate. Put the transfer paper face up on the desired location of your product within the pressing area. If you’re using appliqué transfer or vinyl transfer, cover the transfer paper with a thin cloth to protect it during the heat transfer process.
Applying Heat and Pressure
After the substrate is ready, the transfer paper with the printed design is placed onto it. Heat and pressure are then applied using a heat press machine. The combination of heat and pressure activates the dyes, inks, or vinyl, causing them to adhere to the surface of the material. The temperature and duration of the heat press may vary depending on the materials and transfer method used.
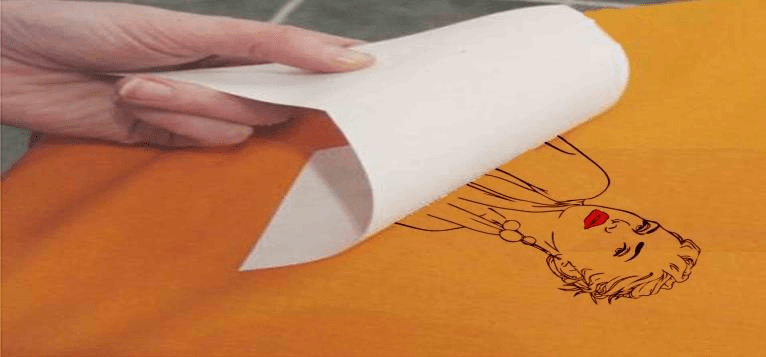
Peeling the Transfer Paper
Once the heat and pressure application is complete, the transfer paper is peeled off, revealing the transferred design on the substrate. Care must be taken during this step to ensure that the design adheres completely to the surface without any smudges or distortions. The final result is a vibrant and durable print.
Types of Transfer Printing
Sublimation Transfer
This method depends on the use of a volatile dye in the printed design. When the paper is heated the dye is preferentially adsorbed from the vapour phase by the textile material with which the heated paper is held in contact. This is commercially the most important of the transfer-printing methods.

Melt Transfer
This method has been used since the 19th century to transfer embroidery designs to fabric. The design is printed on paper using a waxy ink, and a hot iron applied to its reverse face presses the paper against the fabric. The ink melts on to the fabric in contact with it. This was the basis of the first commercially successful transfer process, known as Star printing, developed in Italy in the late 1940s. It is used in the so-called ‘hot-split’ transfer papers extensively used today in garment decoration.
Film Release
This method is similar to melt transfer with the difference that the design is held in an ink layer which is transferred completely to the textile from a release paper using heat and pressure. Adhesion forces are developed between the film and the textile which are stronger than those between the film and the paper. The method has been developed for the printing of both continuous web and garment panel units but is used almost exclusively for the latter purpose. In commercial importance, it is comparable with sublimation transfer printing.

Wet Transfer
Water-soluble dyes are incorporated into a printing ink which is used to produce a design on paper. The design is transferred to a moistened textile using carefully regulated contact pressure. The dye transfers by diffusion through the aqueous medium. The method is not used to any significant extent at the present time.

Types of Heat Transfer Printing
Direct-to-Film (DTF)
Direct-to-Film (DTF) printing is a relatively new heat transfer method that is gaining popularity. It involves printing a design onto a special film using a modified inkjet printer. The film is then pre-treated with a powdered adhesive and heat-pressed onto the garment.

Check out our detailed article on DTF Printing to know all the secrets of it.
Screen Printed Transfers
Screen-printed transfers are created using a traditional screen printing process. A design is burned onto a screen, and ink is then pushed through the screen onto transfer paper. The transfer paper is then heat pressed onto the garment. Each color in the artwork must be printed separately, similar to traditional screen printing techniques.

Vinyl Heat Transfers
HTV is made of a polyurethane material that is cut using a vinyl cutter into the desired design. The design is then placed on the garment and heat pressed to adhere it to the fabric. It comes in a wide variety of colors, finishes, and specialty effects.

Dye sublimation
Dye sublimation is a printing process that uses heat to transfer dye onto fabric. Unlike other heat transfer methods, dye sublimation actually dyes the fabric itself, rather than adhering to a layer of material on top. The ink dyes the fabric, resulting in a print that is vibrant and has no noticeable texture.

Essential Equipment and Supplies for Heat Transfer Printing
To achieve a successful heat transfer and apply a logo using heat transfer printing, you will need the following equipment and supplies:
Computer: A computer with graphic design software is necessary for creating and customizing your design before printing it for heat transfer.
Heat Transfer Printer: Unlike regular printers, a heat transfer printer is specifically designed for heat press applications. It is larger and requires different ink and special transfer paper.
Heat Transfer Ink: Various types of heat transfer inks are available for achieving different finishes. Inkjet ink is commonly used due to its accessibility and affordability. You can also opt for pigment ink for fade resistance or sublimation ink for dye sublimation printing.
Heat Transfer Paper: Heat transfer paper is specially coated with pigment polymer film and wax, which forms a permanent bond with fabric fibers when heated. It is typically available in 13″ by 19″ sheets, allowing for greater design flexibility.
Cutter: A vinyl cutter is necessary for cutting out your design from the heat transfer paper, preparing it for application onto the substrate.
Heat Press: Heat presses come in various sizes and shapes depending on the type of heat transfer application. Clamshell presses and swing-away flatbed machines are suitable for custom t-shirts and flat apparel/accessories, while cylinder-shaped heat presses are used for rounded objects like water bottles and coffee mugs.
Heat Pads: Heat pads are placed on the bottom platen of the heat press and act as the surface for the product during the heat transfer process. They are typically made of heat-resistant foam or silicone rubber.
Heat Tape: Heat-resistant tape is used to secure the heat transfer paper in place on the product during the transfer process.
Heat Resistant Sheeting: Made from materials like Teflon, heat-resistant sheeting is placed between the heating platen and the heat transfer paper to maintain a clean heat press environment and protect the paper from scorching at high temperatures.
Substrates: Substrates are the products you want to decorate using heat transfer printing. They can include drinkware, bags, sweatshirts, polo shirts, custom t-shirts, and more. Consider the substrate as your canvas for creating a heat-transferred masterpiece.
By ensuring you have this essential equipment and supplies, you will be well-equipped to carry out heat transfer printing with precision and achieve impressive results.
Common Problems In Heat Transfer Printing
- Fading or cracking of the prints
- Poor adhesion to the substrate
- Uneven or inconsistent transfers
- Resolving issues with color accuracy
Conclusion
Heat transfer printing is a versatile and efficient method for applying designs onto various surfaces. With its ability to produce vibrant and durable prints, it has become a popular choice in industries ranging from apparel to home décor. Whether you’re looking to personalize clothing, create promotional items, or add a unique touch to your surroundings, heat transfer printing offers endless possibilities.
Referrences:
A textbook on heat transfer by SP Sukhatme
Intermediate heat transfer by Kau-Fui Vincent Wong
FAQs
Can heat transfer prints withstand frequent washing?
Yes, heat transfer prints are highly durable and can withstand repeated washing without fading or peeling.
Is heat transfer printing suitable for small production runs?
Yes, heat transfer printing is cost-effective and ideal for small production runs or personalized items.
Can heat transfer printing reproduce complex designs?
Yes, heat transfer printing allows for intricate and detailed designs, including gradients and photographic images.
Is heat transfer printing environmentally friendly?
Heat transfer printing uses inks and dyes that are safe and eco-friendly, making it a more sustainable printing option.



Your blog brilliantly demystifies the heat transfer printing process! Thanks for the informative breakdown. Your clarity enhances our understanding of this textile technique.
Thanks for this insightful article on heat transfer printing! It provides a clear and comprehensive explanation of the process, making it easier for anyone to understand the intricacies involved. I appreciate the breakdown of each step and the emphasis on the benefits of heat transfer printing. The use of high-quality images further enhances the understanding. Overall, a great resource for anyone looking to delve into or gain a better understanding of heat transfer printing.
This is a topic which is close to my heart… Take care! Where are your contact details though?